As cat owners, it’s important to understand the basic anatomy of our feline companions. Understanding their physique enhances care, health issue identification, and effective communication with our furry friends. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore the key aspects that make cats such fascinating creatures.
Exploring cat anatomy – The cat’s sensory features
Domestic cats (Felis silvestris catus) have a distinct head shape that is a result of their unique facial structure. This shape, characterized by a short muzzle and a relatively large cranium, contributes to their characteristic appearance. Their expressive, vertically-slit pupils offer exceptional depth perception and low-light vision. The sensitive ears of cats are equipped with a wide range of muscles, allowing them to rotate and localize sounds with remarkable precision.
Cat eyes – Insights into cat vision anatomy
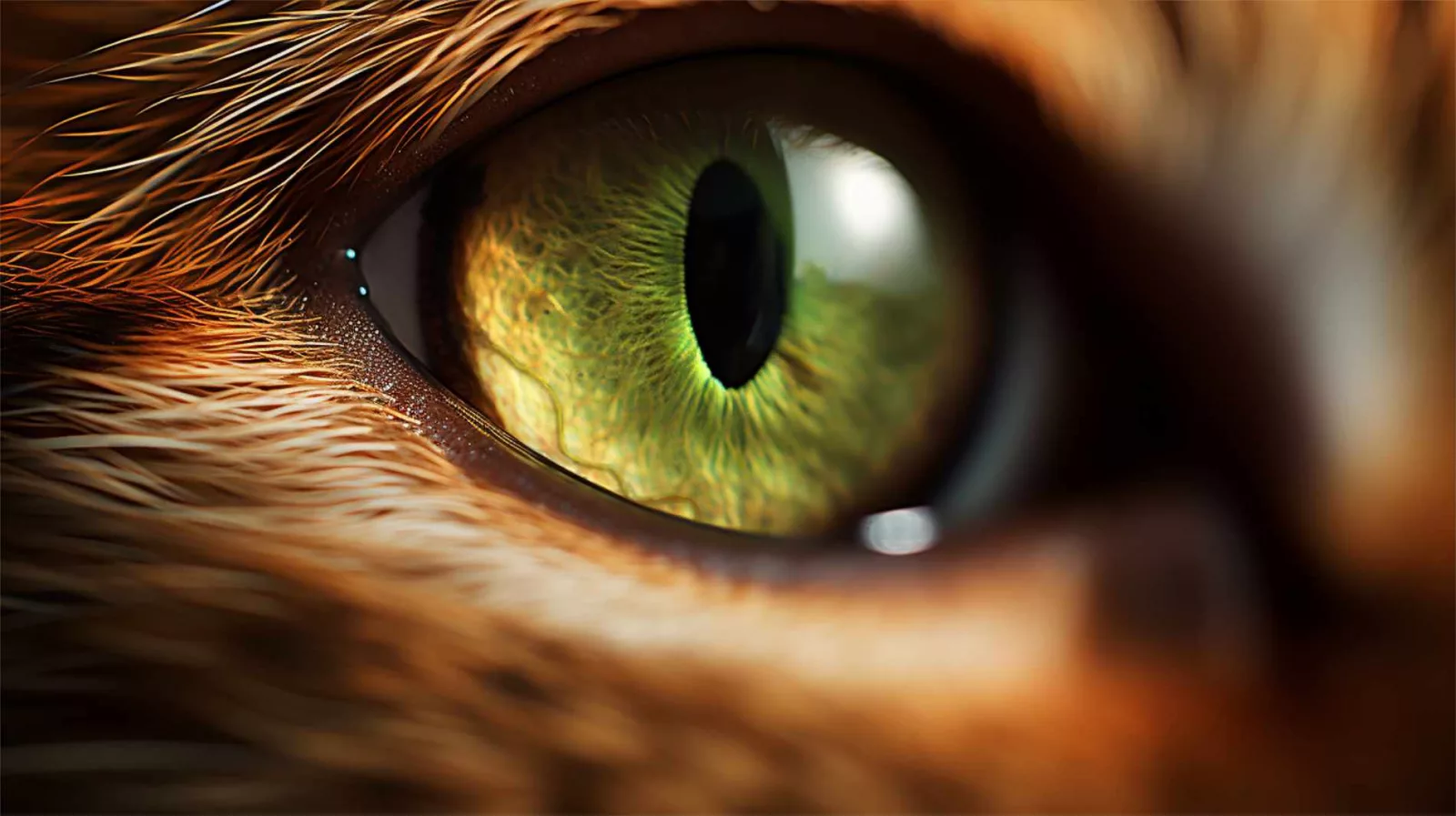

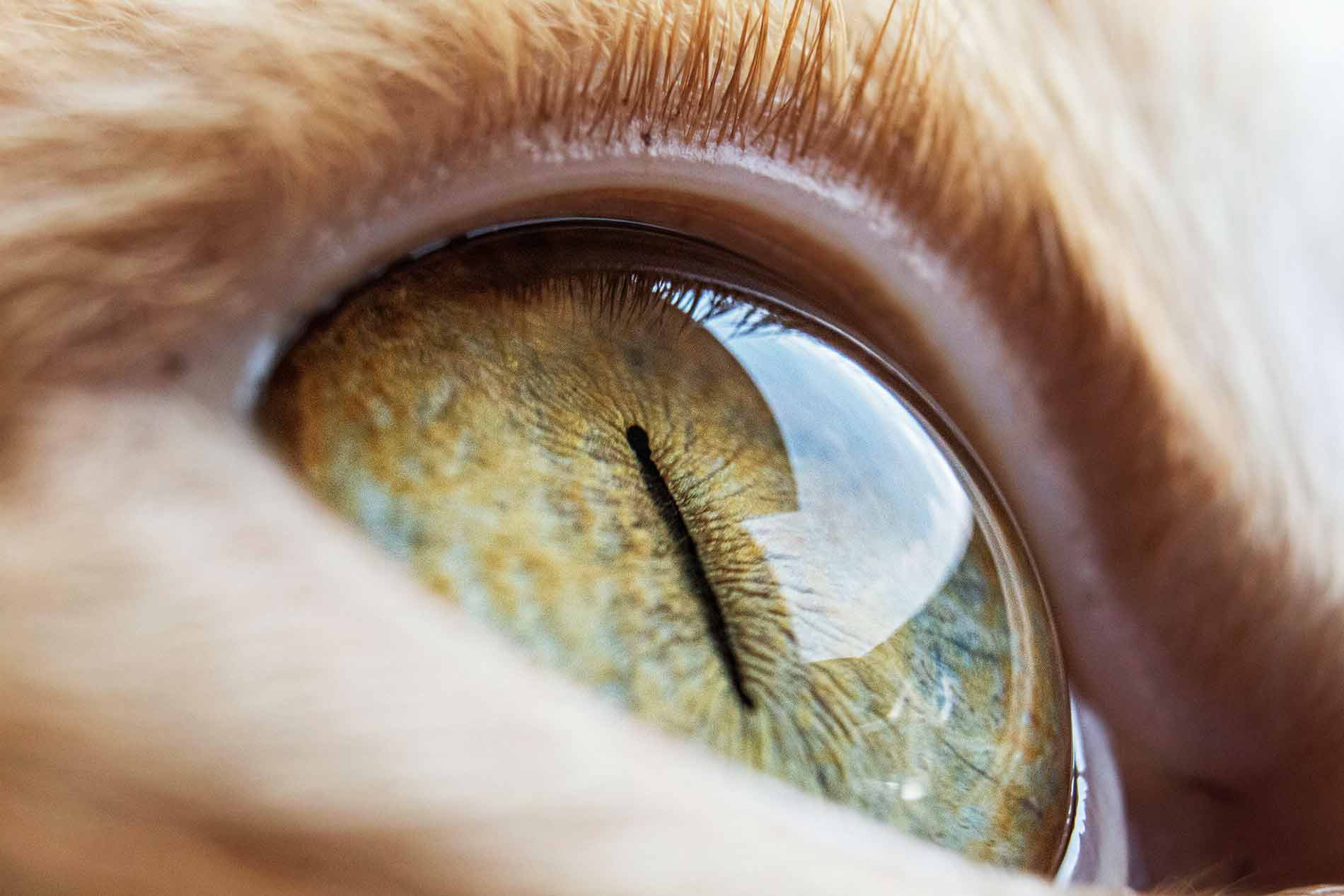
Cat eyes are captivating and possess remarkable characteristics. In addition to their vertical-slit pupils, cats have a specialized reflective layer behind their retinas called the “tapetum lucidum”. This layer acts like a mirror, reflecting light back through the retina and enhancing their night vision. It is what gives cats their distinct eyeshine when exposed to a light source. Furthermore, cats have a higher density of rod cells in their retinas, which are specialized for low-light vision. This adaptation allows them to excel in dimly lit environments, making them adept hunters during dusk and dawn. Cat eyes are truly mesmerizing features that contribute to their prowess as skilled predators.
Perception and communication in feline anatomy – Cat whiskers
Cat whiskers are extraordinary tools for a cat’s spatial awareness and sensory perception. Highly sensitive due to their loaded nerves, whiskers are two to three times thicker than regular cat hair. They also have deeper roots than normal hair. Functioning as delicate touch receptors, they help cats navigate, gauge openings, and detect potential obstacles. By picking up subtle changes in air currents and vibrations (they’re also called “vibrissae”, derived from the Latin word “virbare”), whiskers provide essential environmental information.
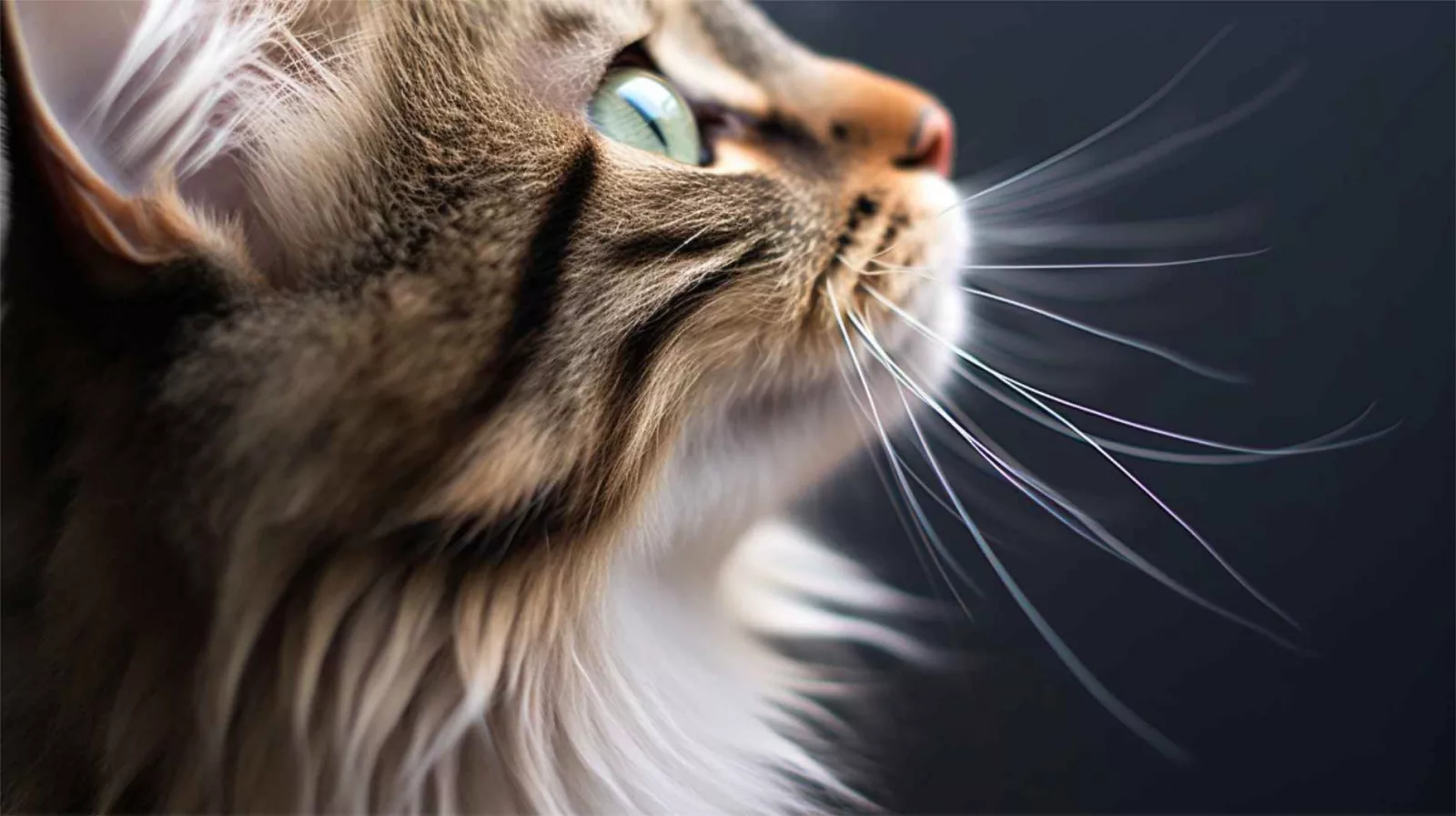

Specialized proprioceptors at the tips enable cats to perceive even the slightest movements, enhancing their precise sensing and mapping abilities. They also play a vital role in feline communication, with flattened whiskers indicating discomfort or unease. Remarkably, cats typically have 12 whiskers on each side, arranged in rows of four, completing their distinctive facial anatomy. In addition to these facial whiskers, cats also have whiskers on their legs, called carpal whiskers. They deliver helpful information when climbing, but also when holding prey.
Cat nose & Jacobson’s organ – Smell and pheromone detection
The nose of a cat is a remarkable organ that plays a vital role in her sensory perception. Scientists have found that the noses of cats are more sensitive than dogs. In fact, cats have a higher number of scent receptors, particularly the V1R receptors responsible for distinguishing between scents. While humans possess only 2 V1R receptors, dogs have 9, and astonishingly, cats possess 30.1 This highlights the remarkable nature of the feline sense of smell, allowing cats to explore the world through scent with unparalleled sensitivity.
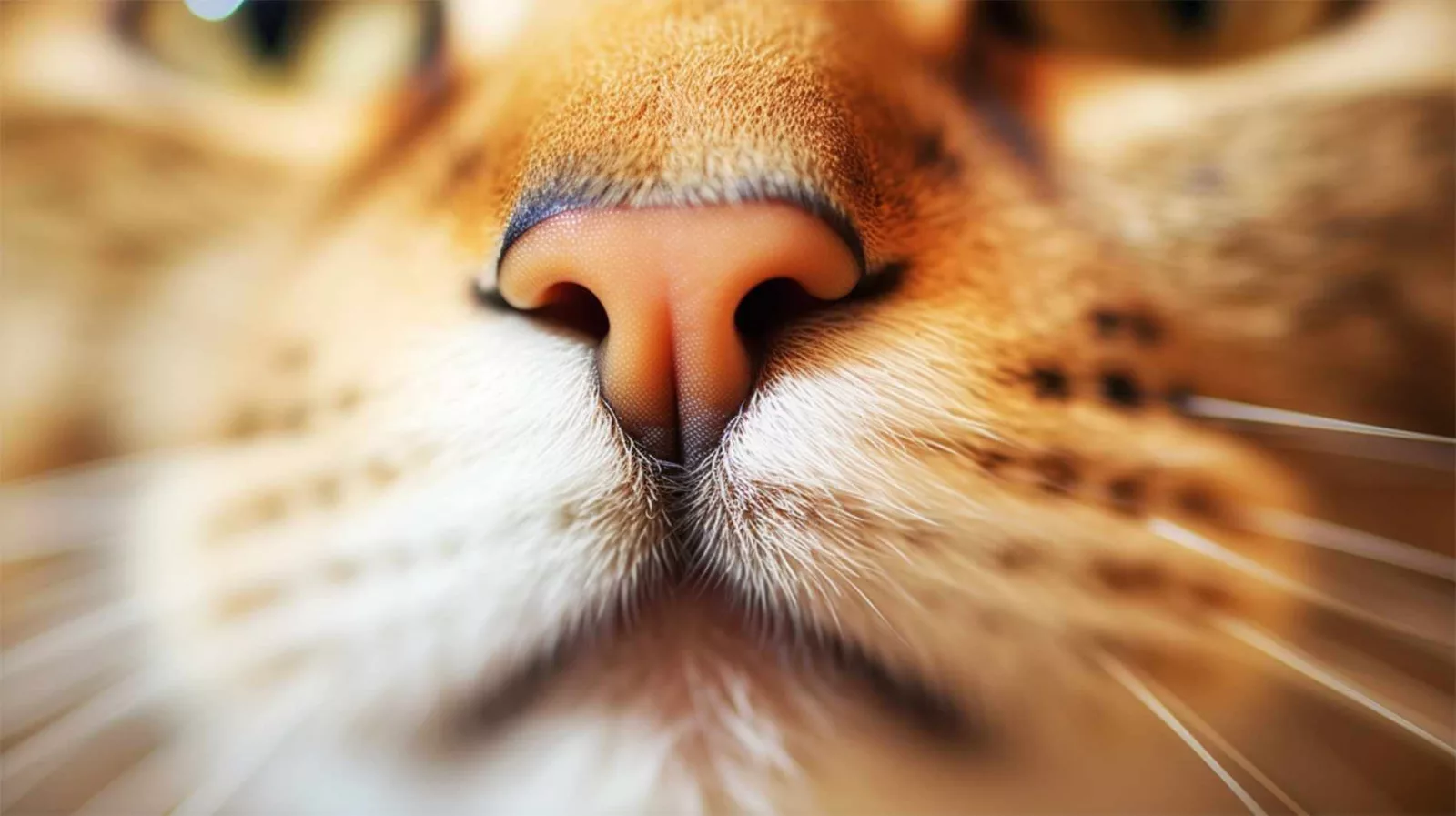


In addition to the external nostrils, a cat has a unique structure known as the Jacobson’s organ, located in the roof of her mouth. This specialized sensory organ, also called the “vomeronasal organ”, plays a significant role in detecting pheromones and other chemical signals emitted by other animals, particularly during mating behaviors. When a cat encounters an intriguing scent, she may open her mouth slightly, a behavior known as the “Flehmen response” (a lot of people jokingly call it the “stink face”). This action helps direct the scent particles to the Jacobson’s organ, allowing the cat to gather more information about her environment and enhance her perception of the world around her.
The cat tongue – taste function in feline anatomy
In the vast realm of cat characteristics, taste and the tongue form an intriguing part of their sensory experience. While cats have a reduced number of taste buds compared to humans and cannot taste sweetness due to the absence of specific taste receptors, their ability to perceive different flavors such as bitterness and sourness is still present. With approximately 470 taste buds, cats exhibit distinct taste preferences influenced by genetics and individual preferences, adding a touch of uniqueness to their culinary experiences.

Beyond taste, the cat’s tongue is a versatile tool with multiple functions. Its rough texture serves both grooming and feeding purposes seamlessly. Acting as a natural comb, it aids in the meticulous grooming rituals that are characteristic of our feline friends. The tiny, backward-facing papillae that cover the tongue’s surface allow cats to rasp and pull meat from bones, aiding in the ingestion of food. This unique adaptation facilitates their dietary needs and enables them to savor their meals with feline finesse.
The foundation – Skeletal system in cats
As with any mammal, the skeleton provides support, protection, and facilitates movement in cats, too. One remarkable aspect of a cat’s skeletal system is its flexible spine, composed of more vertebrae than in other mammals. This allows cats to showcase remarkable agility, enabling them to twist and turn mid-air with astonishing grace. Unlike the more rigid spines of humans or dogs, a cat’s spine allows them to navigate narrow spaces and land gracefully from great heights.

Cats have a distinctive skeletal structure that contributes to their agility. Despite having a higher number of bones, averaging 244 compared to 206 in humans, it’s remarkable that cats lack a bone that humans possess – the collarbone (clavicle). Their skeletal structure also features specialized adaptations such as a long tail, which acts as a balancing tool during complex maneuvers.
With their flexible spine, elongated lumbar vertebrae, and uniquely elastic cushioning in their vertebral discs, cats display exceptional agility and swift movements. These impressive skeletal adaptations underpin their extraordinary ability to navigate their surroundings and perform intricate maneuvers with ease.
Powering cat anatomy – Muscles and locomotion
Cats rely on a complex network of muscles that provide the strength and agility necessary for their remarkable movements. Each muscle group plays a crucial role in a cat’s exceptional locomotion and predatory abilities.
The leg muscles of a cat, such as the quadriceps and hamstring groups, are highly developed and contribute to their impressive jumping and running capabilities. These muscles contract and extend with remarkable force, propelling cats into extraordinary leaps and swift sprints.


In addition to the leg muscles, the torso muscles in cats are equally important. The abdominal muscles, including the obliques and rectus abdominis, provide stability and support during intricate maneuvers, allowing cats to execute quick turns and maintain exceptional balance.
Furthermore, cats possess a high proportion of fast-twitch muscle fibers, which are built for short, powerful bursts of energy. This muscular composition, combined with their flexible spines and agile joints, grants cats unparalleled agility and speed.
Did you know cats walk on tiptoe all the time?
Conclusion
Understanding cat anatomy enhances our ability to provide optimal care and appreciate the intricate design of our feline friends. By recognizing their external features, marveling at the skeletal system, acknowledging the power of their muscles, and embracing their extraordinary senses, we deepen our bond with these wonderful creatures. Take a moment to observe and appreciate the fascinating cat anatomy of your beloved feline companion.
If you enjoyed this beginner’s guide, let your friends know and share it with them.